Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) refers to the capacity of microorganisms to resist the effects of otherwise inhibitory chemicals - an attribute that can be intrinsic or acquired.
The Welsh Government commission for this review was to identify how AMR:
- “enters and spreads via the rural water environment”
- “impacts on animal and human health”
- can be “tackled at Welsh-level using an integrated policy approach to ensure the effectiveness of antibiotics for future generations.”
This Evidence Review is intended to inform policy on the delivery of the Welsh Government’s 5-year ‘Antimicrobial resistance in animals and the environment implementation plan’. Specifically, it will inform the third component – Minimising the spread of AMR through the environment, with a focus on water sources. This component commits to support research into identifying evidence gaps and improving understanding of the hazards and risks from AMR in the environment.
The spread of AMR though mobile genetic elements is at the core of the global spread of novel antimicrobial resistance genes and a mechanism driving the increase in drug-resistant infections – a threat that currently costs the NHS an estimated £30 billion per year.
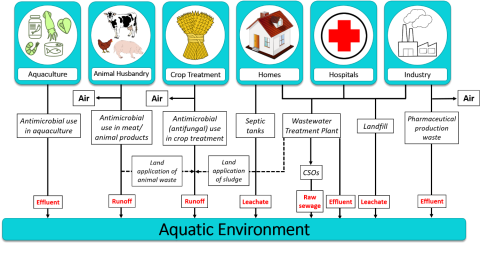
Antimicrobials (antivirals, antibacterials, antifungals, antiprotozoals, anthelmintics) represent a fraction of all chemicals that are known to select for or help to maintain antimicrobial resistance genes in the environment. These antimicrobial resistance-driving chemicals include metals, biocides, pesticides and many other commonly found environmental pollutants.
Areas of significant anthropogenic impact tend to also harbour more AMR; these locations include manufacturing and industry discharge, agriculture, municipal wastewater (wastewater treatment plants, combined-sewer outfalls, sewage sludge) and meat animal, egg, sport animal and dairy production activities (feed, chemotherapy, biosecurity, manure, slurry).
The review team identified knowledge gaps for follow-up research and possible policy directions, compatible with the wider legislation framework, notably the Well-being of Future Generations (Wales) Act 2015 and Environment (Wales) Act 2016 and associated UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Related
The Welsh Government's Animal and Environment Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Annual Review 2020/21

